We are not a registered HMO/Medicare/Medicaid provider instead, try our Membership Plan
Sleep Apnea
Understanding and Treating Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a potentially life-threatening sleep disorder characterized by repeated pauses in breathing during sleep. The term sleep apnea is derived from the Greek etymology meaning “without breath”. Breathing pauses can last anywhere from several seconds to minutes, and happen as often as 30 times or more per hour. Ongoing disrupted breathing causes an imbalance between the carbon dioxide and oxygen levels in the bloodstream, as not enough carbon dioxide is exiting and not enough oxygen is entering the body.
Sensing this imbalance, the brain sends a message to the body, telling it to wake up to restart the breathing process. People with sleep apnea will partially awake as they struggle to breathe, and this is often accompanied by loud snoring or choking sensations. Because people with sleep apnea don’t always completely awake during the episodes, they are often unaware they have a sleeping disorder and it can remain undiagnosed.
There are two main types of this disorder; central sleep apnea which occurs when the brain fails to send important signals to the breathing muscles, and obstructive sleep apnea which occurs when air cannot flow through the nose or mouth even though the body is still trying to breathe. Obstructive sleep apnea is far more prevalent and easily treatable by the dentist.
Common signs of obstructive sleep apnea can include severe early morning headaches, sleepiness in the daytime, and insomnia. Fortunately, the dentist is equipped with the necessary technology and expertise to treat sleep apnea in several different ways.
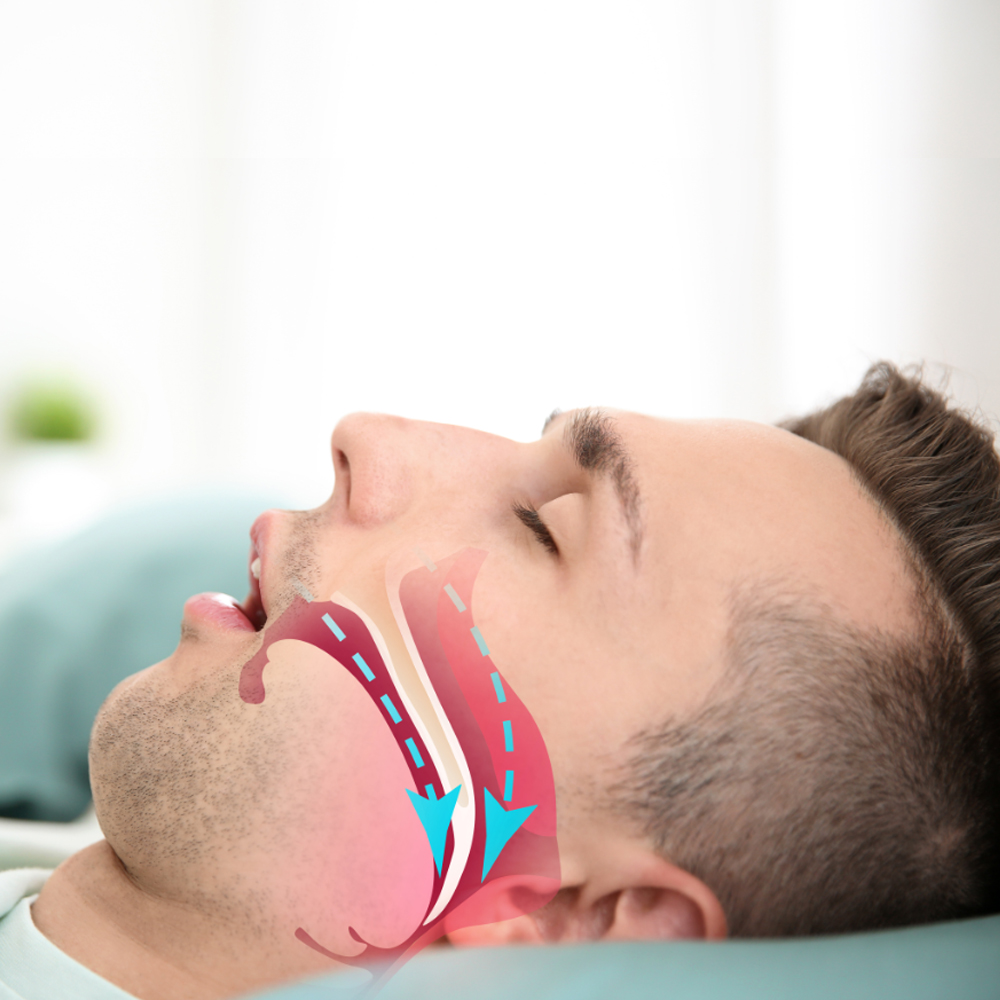
Reason for treating sleep apnea
Sleep apnea is a serious sleep disorder where breathing repeatedly stops during sleep. The term comes from Greek, meaning "without breath." Pauses in breathing can last from seconds to minutes and occur over 30 times an hour, disrupting oxygen and carbon dioxide balance in the blood. The brain signals the body to wake up and restart breathing, often causing loud snoring or choking. Many people with sleep apnea are unaware they have it as they don't fully wake up during episodes.
There are two main types: central sleep apnea, where the brain fails to signal breathing muscles, and obstructive sleep apnea, where airflow is blocked despite the body's efforts to breathe. Obstructive sleep apnea is more common and treatable by dentists.
Signs of obstructive sleep apnea include morning headaches, daytime sleepiness, and insomnia. Dentists have the expertise and technology to effectively treat this condition.

What does sleep apnea treatment involve?
Initially, the dentist will want to conduct tests in order to investigate, diagnose, and pinpoint a suitable treatment. The dentist can offer many different treatment options which depend largely on the exact diagnosis and the health of the patient. The dentist may advise the patient to halt some habits that aggravate sleep apnea such as smoking, alcohol consumption, and tranquilizer use.
Sleeping masks were traditionally used to keep the patient’s airways open while they slept, but nowadays there are some less intrusive options. Dental devices that gently tease the lower jaw forward are very effective in preventing the tongue from blocking the main air passage. These dental devices are gentle, easy to wear, and often help patients avoid unwanted surgeries.
A more permanent solution is to have surgery that sections the lower jaw and helps pull the bone holding the tongue forward slightly. This surgery has an impressive success rate and is simple for the dentist or oral surgeon to perform. The dentist needs to formally make a diagnosis of each individual case before recommending the best course of action.


